
LibRan pseudo-random number generator library
The LibRan package is a library of various pseudo-random number generators along with their exact probability and cumulative probability density functions. The libary contains its own optimized sequential congruential uniform pseudo-random number generator on the interval 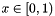 ; along with useful tools such as methods for collecting statistics into bins.
; along with useful tools such as methods for collecting statistics into bins.
Each of the random variate distributions rely on a number of internal attributes to customize the distribution. The library is written in an object oriented fashion (in C) such that each object's attributes and random number generator is separate from every other object. There are also generic routines for calling the various specialized routines for the given random variate distribution.
Required Library Methods
Each random variate included here has at least three provided methods, and for two numeric precisions - (f = float and d = double). The data or numeric precision is given by the enum LR_data_type in libran.h.
| Routine | Generic Fn | Description |
|---|---|---|
| LR?_*_RAN | LR?_RAN | Random variate generator |
| LR?_*_PDF | LR?_PDF | Random variate probability distribution function |
| LR?_*_CDF | LR?_CDF | Random variate cumulative distribution function |
Where 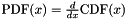 , and
, and 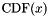 is a monotonically non-decreasing function such that
is a monotonically non-decreasing function such that
![\[ \mbox{CDF}(x_1) \le \mbox{CDF}(x_2) \mbox{ where } x_1 < x_2 \]](form_3.png)
and
![\[ 0 \le \mbox{CDF}(x) \le 1 \mbox{ for all } x \]](form_4.png)
The generic functions are found in LRdf.c.
[For discrete distributions the probability mass function (PMF) is taken here as synonymous with the probability distribtuion function (PDF).]
Random Variate Distributions
There are a number of built-in random variate distributions and the complete list of allowed distribution types is given by the enum LR_type in libran.h. They fall into a few types as follows:
Full Infinite Range
These random variate distributions will generate variates where 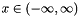 . These distributions are defined with attributes m and s representing the mean or mode and the width of the distribution.
. These distributions are defined with attributes m and s representing the mean or mode and the width of the distribution.
| Type | Source | Distribution Description |
|---|---|---|
| unif | LRunif.c | uniformly on given interval |
| gausbm | LRgaus.c | Gaussian or Normal using Box-Muller method |
| gausmar | LRgaus.c | Gaussian or Normal using Marsaglia method |
| cauchy | LRcauchy.c | Cauchy using inverse method |
| cauchymar | LRcauchy.c | Cauchy using Marsaglia method |
Semi-Infinite Range
These random variate distributions will generate variates where 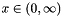 .
.
| Type | Source | Distribution Description |
|---|---|---|
| nexp | LRnexp.c | negative exponential |
Finite Range
These random variate distributions will generate variates on a finite interval 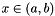 .
.
| Type | Source | Distribution Description |
|---|---|---|
| gsn2 | LRgsn.c | Gaussian-like (sawtooth) |
| gsn4 | LRgsn.c | Gaussian-like (simple bell curve) |
| gsn12 | LRgsn.c | Gaussian-like (close Gaussian approximation) |
User Defined
These distributions have user-defined shapes.
| Type | Source | Distribution Description |
|---|---|---|
| lspline | LRlspline.c | Linear spline PDF on [a,b] |
| piece | LRpiece.c | Histogram-like PDF on [a,b] |
| inverse | LRinv.c | User defined CDF |
Discrete
These distributions return discrete (integer values) which are distributed according to the probability mass function (PMF), but denoted here as the probability density function (PDF).
| Type | Source | Distribution Description |
|---|---|---|
| poisson | LRpoisson.c | Events in a fixed interval |
Example Code
Here is an example code showing how to use the LR_obj and LR_bin objects and how to set-up the LR_bin tally bins. The expected values rely on calculating the difference of CDFs at the boundaries.
The median is at 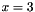 with a width of 2. This code can be used as-is by just changing the
with a width of 2. This code can be used as-is by just changing the LR_type from gausbm to either gausmar, gsn12, cauchy, or cauchymar. The code can be simply changed for those random variate distributions with definite endpoints a and b.
 1.8.13
1.8.13